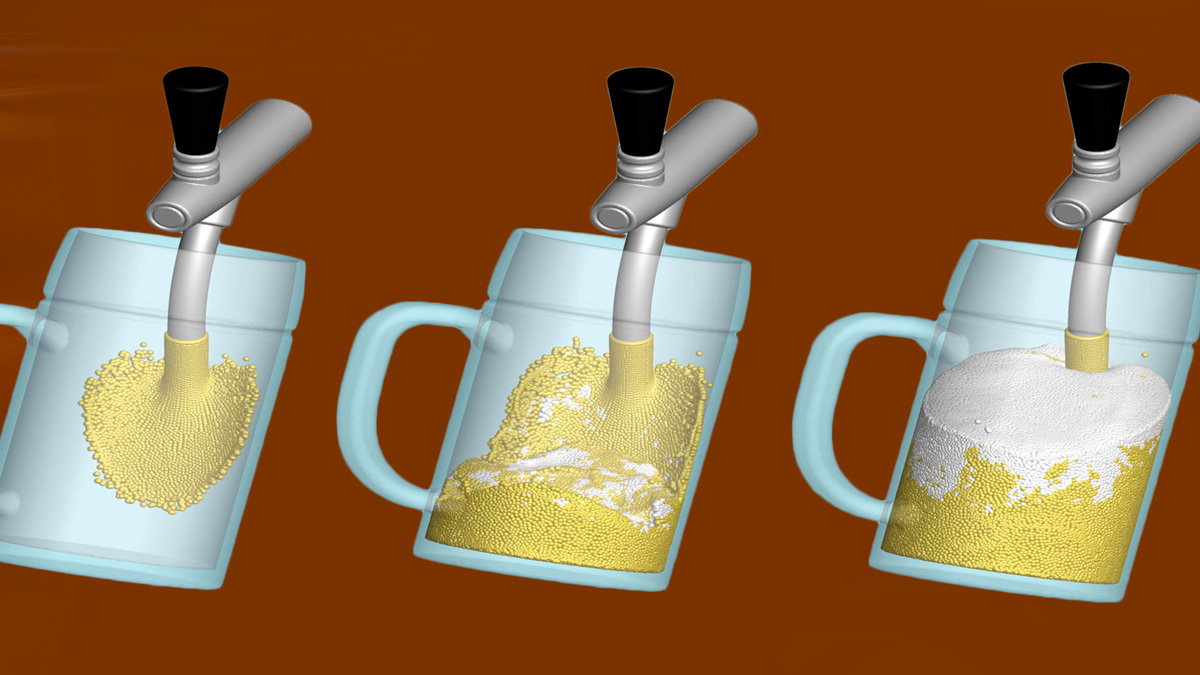
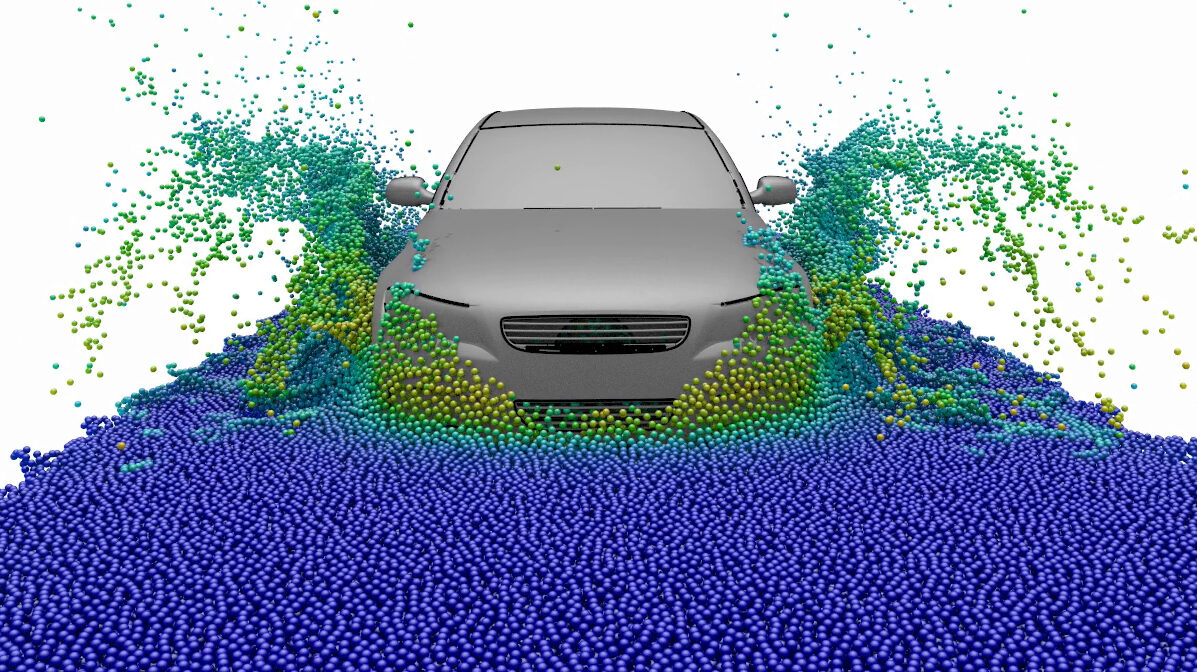
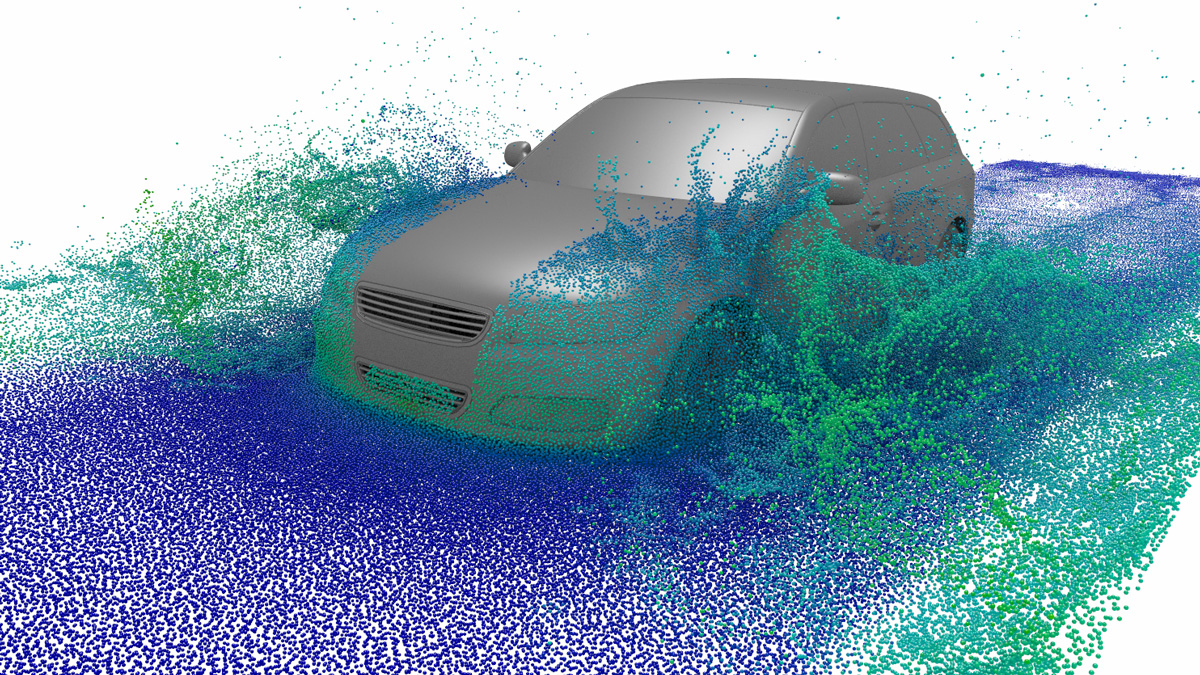
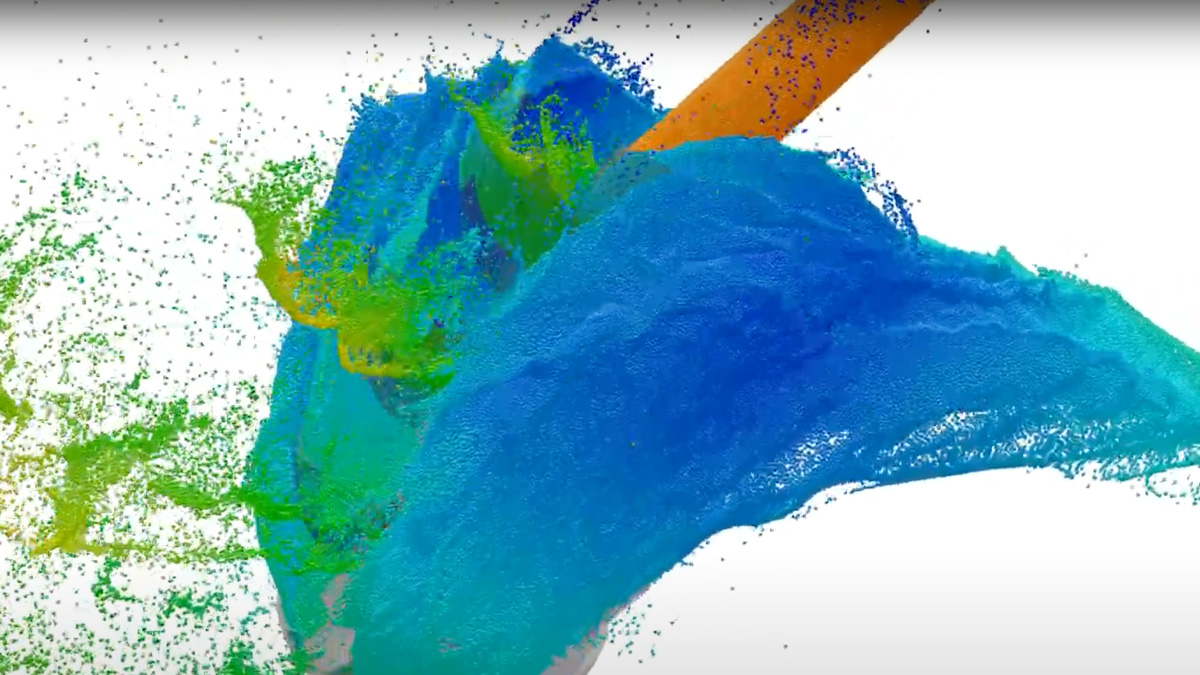
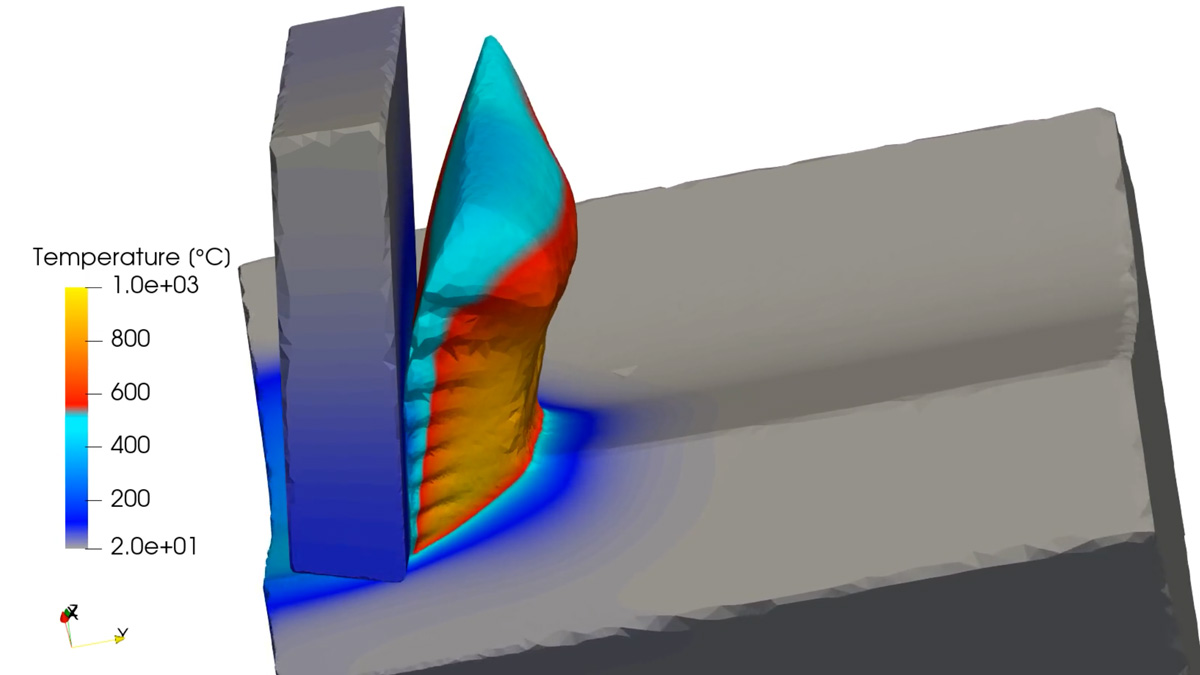
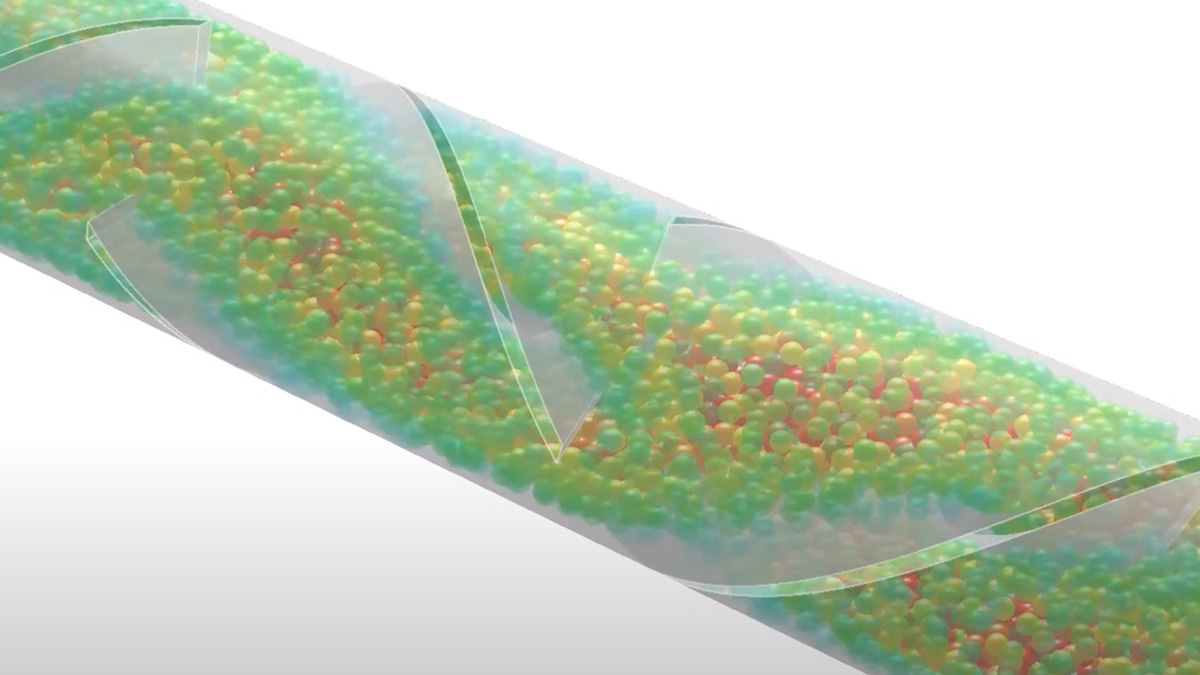
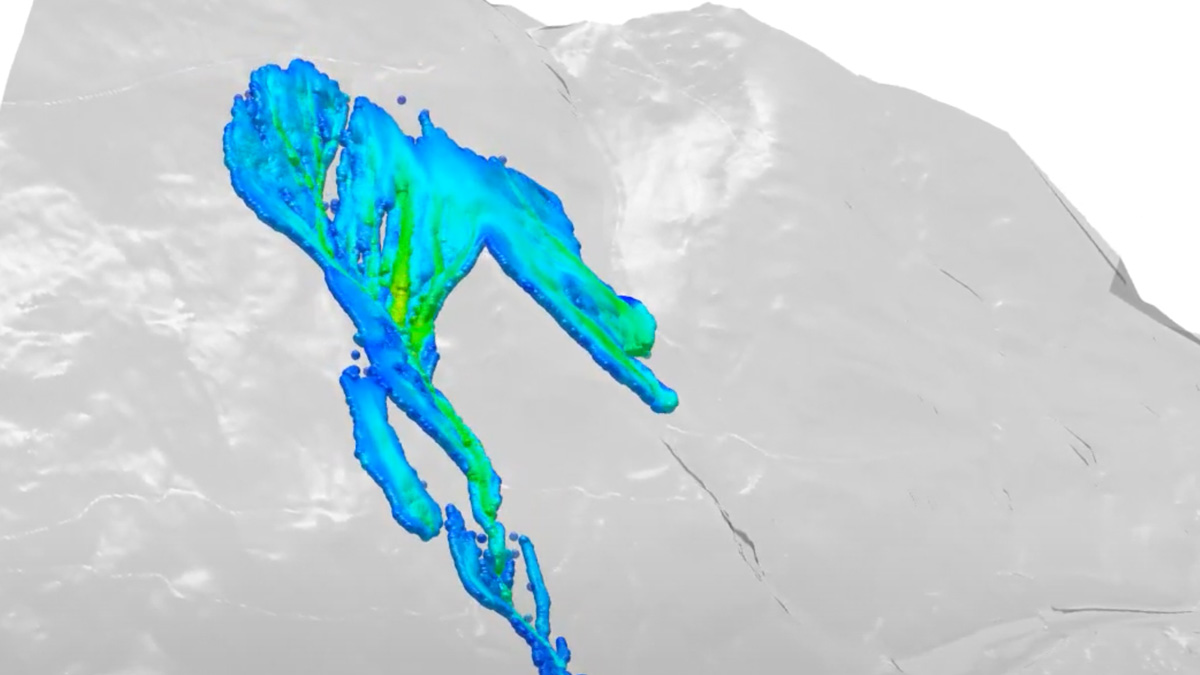
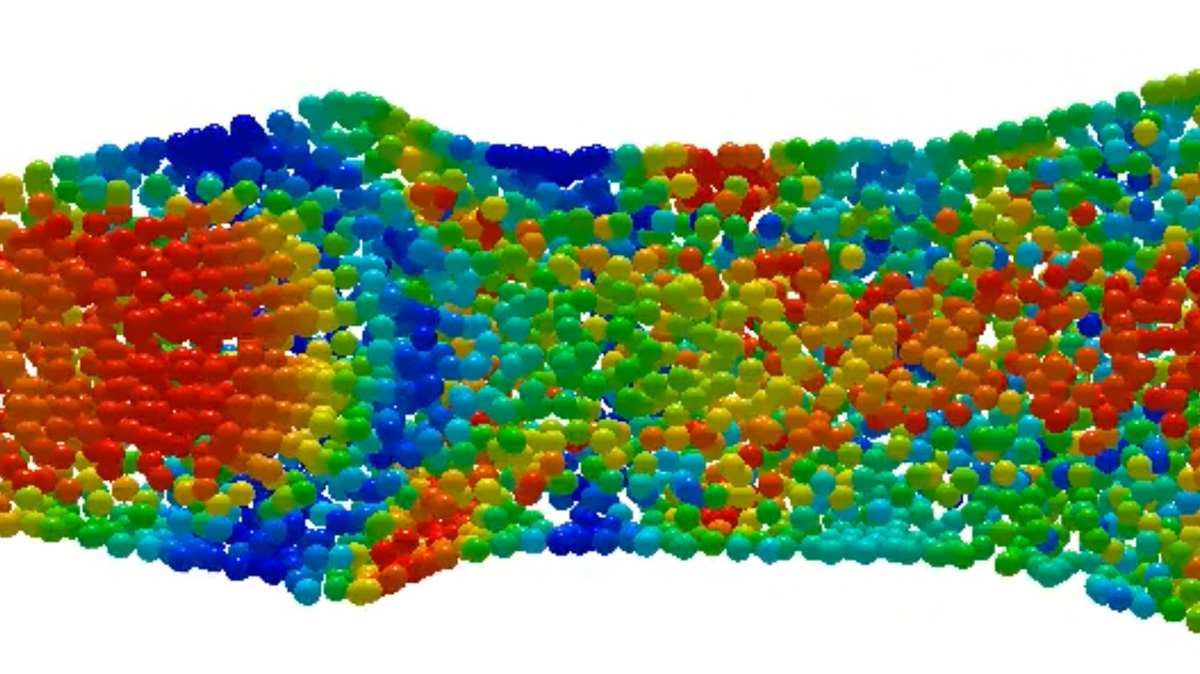
In common simulation workflows, the preprocessing step consisting of mesh generation and adaption is very time consuming. MESHFREE follows an innovative point cloud approach, avoiding meshes, and thus enabling engineers to design their products much faster.
Benefit & added value
A general continuum mechanics approach is the basis for models of a vast variety of nonlinear physical phenomena such as non-Newtonian fluids and other complex materials. Hence, MESHFREE simulations can cover a wide range of applications such as water management, avalanches, foam formation, metal cutting, sophisticated fluid-structure interactions and many more.
In contrast to classical mesh-based approaches, MESHFREE uses an automatically managed point cloud that adapts itself efficiently to the simulation domain – even if the simulation domain changes rapidly due to moving geometries or large deformations.
MESHFREE is a powerful simulation tool for:
- fluid dynamics
- continuum mechanics
- multiphase scenarios
Advantages & Features
The unique features of MESHFREE enable numerical simulation of scenarios that are currently completely out of reach of other simulation tools: Simulating a water-crossing car or turbine abrasion. Additionally, the computation can be faster in scenarios that are difficult for mesh-based methods such as free surface flows.
Application areas
References & Partners
Comparison of MESHFREE to Mesh-Based
| Aspect | Mesh-based Method | MESHFREE |
|---|---|---|
| Preparing a 3D Simulation | 3D meshing. High quality mesh software needed | Requires 2D surface mesh only. MESHFREE automatically fills the computation domain with the point cloud. |
| Free Surface Flows | e.g. Volume-of-fluid, computation of full domain | In MESHFREE, only the part of the simulation domain that is filled with the fluid needs to be computed yielding a computational advantage. |
| Rapidly Moving Geometries | Remeshing (potentially computational expensive) | The point cloud automatically adapts to the changing fluid domain. Full flexibility regarding changing topologies. |
| Local Refinement | Remeshing (potentially computational expensive) | Also full flexibility for local refinement – even while you are computing the simulation with our computational steering feature! |
| Interpretation of Results | Postprocessing | The points of the point cloud move with the velocity of the fluid. This yields a very intuitive way to visualize and interpret the computational results. |